An Integrated Quadruped-Hexarotor System
Collaboration of an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and a quadruped robot to conduct exploration tasks in flight-impeded zones.
 This research was conducted in the laboratory of Cooperative Intelligence of Unmanned Systems (CIUS) led by Prof. Wei Dong. Aiming at exploration and rescue tasks in flight-impeded areas, we designed an integrated quadruped-hexarotor system. UAVs are flexible and efficient in transporting the ground vehicle to the task spot, and quadruped robots are of high adaptiveness in complex environments. The collaboration can combine the advantages of aerial and quadruped vehicles.
This research was conducted in the laboratory of Cooperative Intelligence of Unmanned Systems (CIUS) led by Prof. Wei Dong. Aiming at exploration and rescue tasks in flight-impeded areas, we designed an integrated quadruped-hexarotor system. UAVs are flexible and efficient in transporting the ground vehicle to the task spot, and quadruped robots are of high adaptiveness in complex environments. The collaboration can combine the advantages of aerial and quadruped vehicles.
Collaboration Process
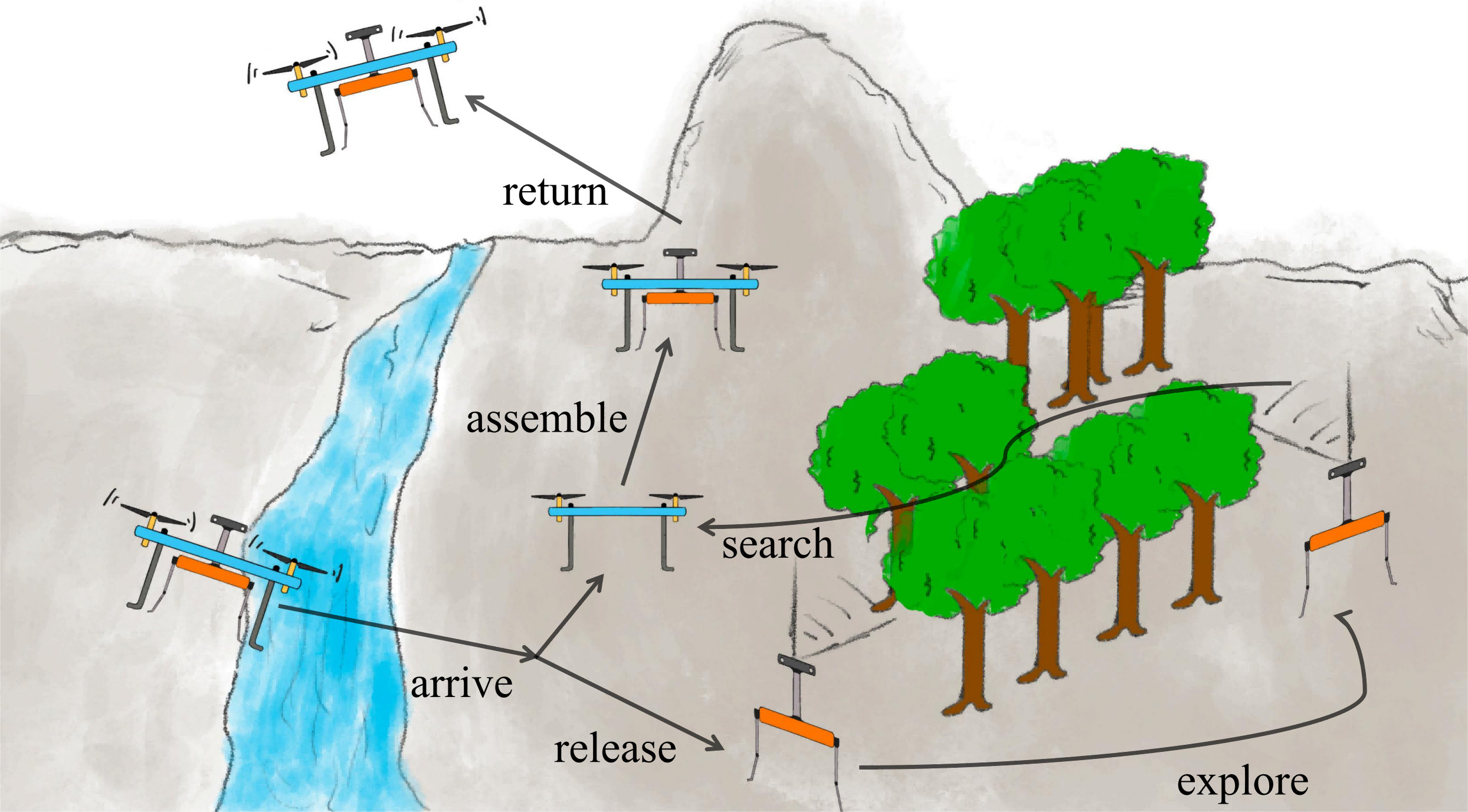 As illustrated in the cartoon picture above, the hexarotor delivers the quadruped over ground obstacles to somewhere near task sites and releases it. Then the quadruped conducts exploration tasks in complex flight-impeded areas while the UAV remains unmoved. After the mission, the quadruped searches for the hexarotor via onboard localization and vision systems, assembling the two robots for return. Only one onboard computer carried by the quadruped is utilized during the whole process, reducing the overall weight and cost.
As illustrated in the cartoon picture above, the hexarotor delivers the quadruped over ground obstacles to somewhere near task sites and releases it. Then the quadruped conducts exploration tasks in complex flight-impeded areas while the UAV remains unmoved. After the mission, the quadruped searches for the hexarotor via onboard localization and vision systems, assembling the two robots for return. Only one onboard computer carried by the quadruped is utilized during the whole process, reducing the overall weight and cost.
System Design
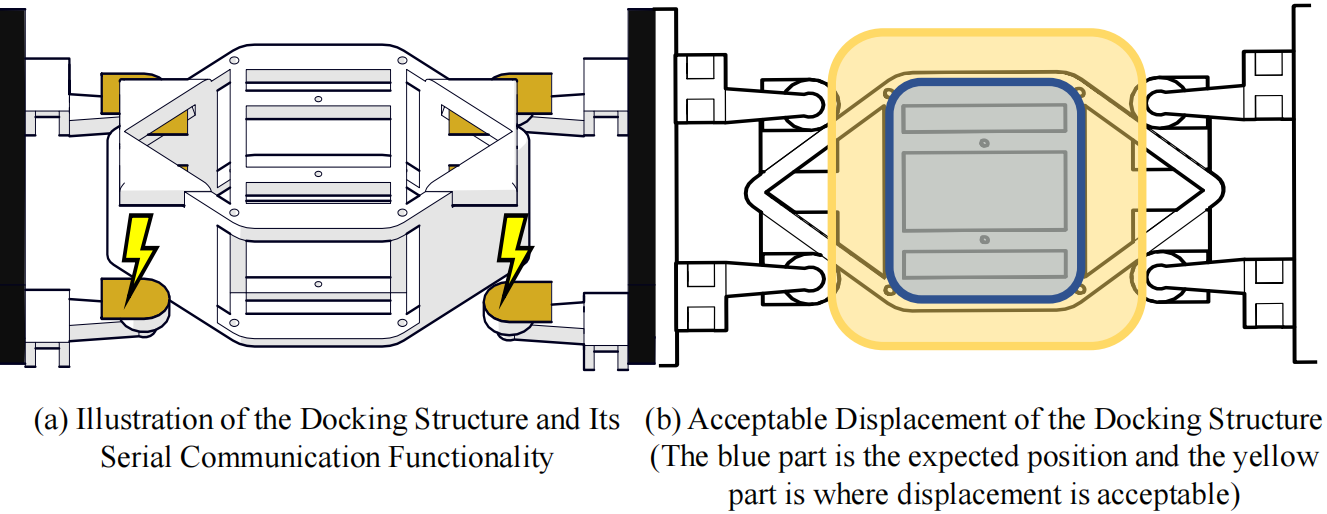 In transportation, the UAV and the quadruped robot are closely contacted. We exploited this and developed an adaptive docking system, with which the the AUV can capture the quadruped without requiring high localization accuracy. And this system enabled two vehicles to share computing resources with four electrodes for serial communication.
In transportation, the UAV and the quadruped robot are closely contacted. We exploited this and developed an adaptive docking system, with which the the AUV can capture the quadruped without requiring high localization accuracy. And this system enabled two vehicles to share computing resources with four electrodes for serial communication.
We also implemented a vision-based remote localization package to enable the quadruped finding the hexarotor quickly after the tasks finish. Details of the system can be found in our published paper in 2021 IEEE M2VIP.